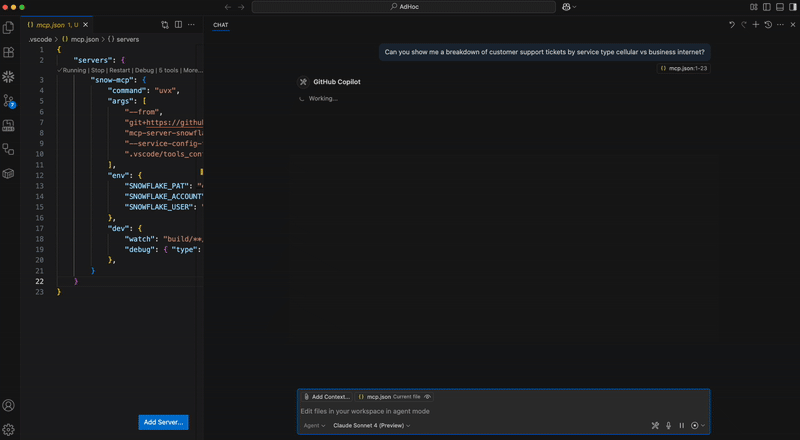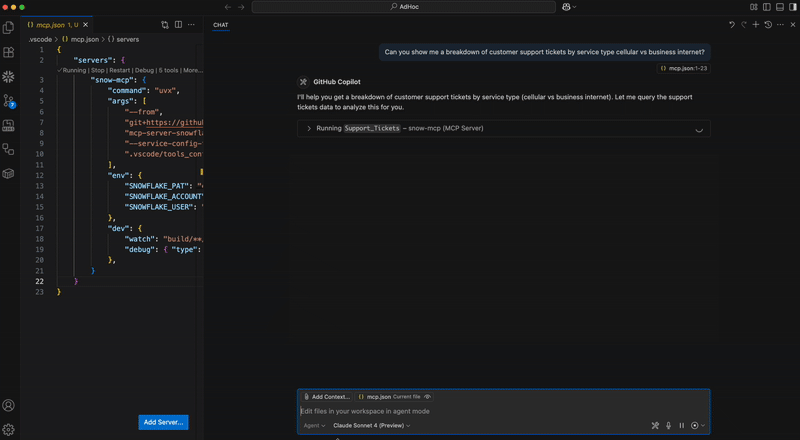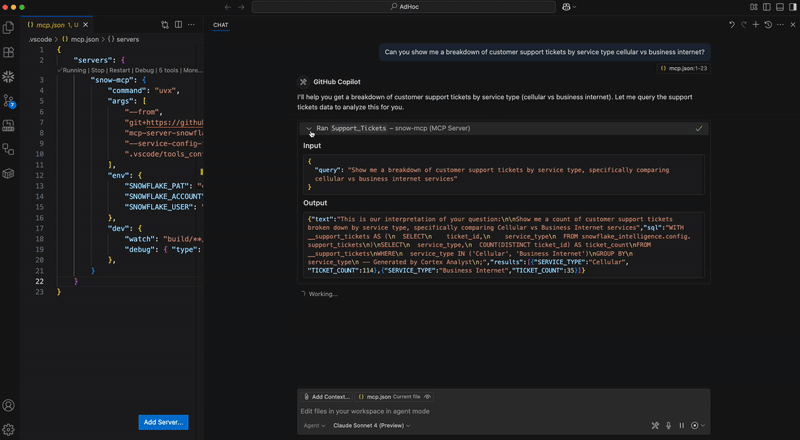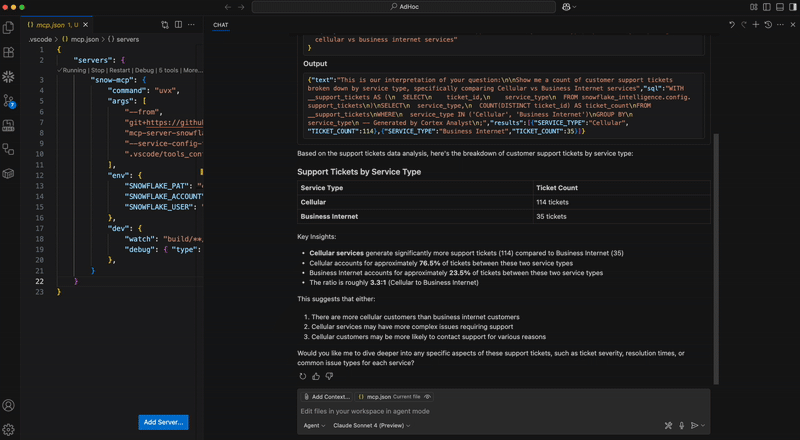
This Snowflake MCP server provides tooling for Snowflake Cortex AI features, bringing these capabilities to the MCP ecosystem. When connected to an MCP Client (e.g. Claude for Desktop, fast-agent, Agentic Orchestration Framework), users can leverage these Cortex AI features.
The MCP server currently supports the below Cortex AI capabilities:
- Cortex Search: Query unstructured data in Snowflake as commonly used in Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications.
- Cortex Analyst: Query structured data in Snowflake via rich semantic modeling.
- Cortex Agent: (Coming Soon) Agentic orchestrator across structured and unstructured data retrieval
- SQL Execution: Execute SELECT, SHOW, DESCRIBE, and EXPLAIN queries directly on Snowflake for data analysis and exploration.
A simple configuration file is used to create tooling for the various Cortex AI features. An example can be seen at services/tools_config.yaml and a template is below. Many Cortex Search and Cortex Analyst services can be added. Ideal descriptions are both highly descriptive and mutually exclusive. The path to this configuration file will be passed to the server and the contents used to create MCP server tools at startup.
search_services: # List all Cortex Search services
- service_name: "<service_name>"
description: > # Should start with "Search service that ..."
"<Search services that ...>"
database_name: "<database_name>"
schema_name: "<schema_name>"
columns: [] # Optional: List of columns to return for each relevant result (default: [])
limit: 10 # Optional: Limit on the number of results to return (default: 10)
- service_name: "<service_name>"
description: > # Should start with "Search service that ..."
"<Search services that ...>"
database_name: "<database_name>"
schema_name: "<schema_name>"
columns: [] # Optional: List of columns to return for each relevant result (default: [])
limit: 10 # Optional: Limit on the number of results to return (default: 10)
analyst_services: # List all Cortex Analyst semantic models/views
- service_name: "<service_name>" # Create descriptive name for the service
semantic_model: "<semantic_yaml_or_view>" # Fully-qualify semantic YAML model or Semantic View
description: > # Should start with "Analyst service that ..."
"<Analyst service that ...>"
- service_name: "<service_name>" # Create descriptive name for the service
semantic_model: "<semantic_yaml_or_view>" # Fully-qualify semantic YAML model or Semantic View
description: > # Should start with "Analyst service that ..."
"<Analyst service that ...>"
The MCP server uses the Snowflake Python Connector for authentication and connection. For security reasons, this MCP server only supports external browser authentication.
Connection parameters can be passed as CLI arguments and/or environment variables. The server enforces the use of externalbrowser authentication, which provides secure, interactive authentication through your web browser and supports:
- Single Sign-On (SSO) with Okta, AD FS, or any SAML 2.0-compliant identity provider
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) through your identity provider
- Secure authentication without storing passwords or private keys
Connection parameters can be passed as CLI arguments and/or environment variables:
| Parameter | CLI Arguments | Environment Variable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Account | --account | SNOWFLAKE_ACCOUNT | Account identifier (e.g. xy12345.us-east-1) |
| Host | --host | SNOWFLAKE_HOST | Snowflake host URL |
| User | --user, --username | SNOWFLAKE_USER | Username for authentication |
| Role | --role | SNOWFLAKE_ROLE | Role to use for connection |
| Warehouse | --warehouse | SNOWFLAKE_WAREHOUSE | Warehouse to use for queries |
| Authenticator | --authenticator | SNOWFLAKE_AUTHENTICATOR | Must be set to "externalbrowser" (enforced) |
| Connection Name | --connection-name | - | Name of connection from connections.toml (or config.toml) file |
Important
Security Notice: This MCP server only supports externalbrowser authentication. Password-based authentication, private key authentication, and other methods are not supported for security reasons. The server will validate and enforce this requirement at startup.
The MCP server is client-agnostic and will work with most MCP Clients that support basic functionality for MCP tools and (optionally) resources. Below are some examples.
To integrate this server with Claude Desktop as the MCP Client, add the following to your app's server configuration. By default, this is located at
- macOS: ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
- Windows: %APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
Set the path to the service configuration file and configure your connection method.
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcp-server-snowflake": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"--from",
"git+https://github.com/Snowflake-Labs/mcp",
"mcp-server-snowflake",
"--service-config-file",
"<path to file>/tools_config.yaml",
"--connection-name",
"default"
]
}
}
}
Register the MCP server in cursor by opening Cursor and navigating to Settings -> Cursor Settings -> MCP. Add the below.
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcp-server-snowflake": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": [
"--from",
"git+https://github.com/Snowflake-Labs/mcp",
"mcp-server-snowflake",
"--service-config-file",
"<path to file>/tools_config.yaml",
"--connection-name",
"default"
]
}
}
}
Add the MCP server as context in the chat.
For troubleshooting Cursor server issues, view the logs by opening the Output panel and selecting Cursor MCP from the dropdown menu.
Update the fastagent.config.yaml mcp server section with the configuration file path and connection name.
# MCP Servers
mcp:
servers:
mcp-server-snowflake:
command: "uvx"
args: ["--from", "git+https://github.com/Snowflake-Labs/mcp", "mcp-server-snowflake", "--service-config-file", "<path to file>/tools_config.yaml", "--connection-name", "default"]
For prerequisites, environment setup, step-by-step guide and instructions, please refer to this blog.
The MCP Inspector is suggested for troubleshooting the MCP server. Run the below to launch the inspector.
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector uvx --from "git+https://github.com/Snowflake-Labs/mcp" mcp-server-snowflake --service-config-file "<path_to_file>/tools_config.yaml" --connection-name "default"
- This MCP server only supports externalbrowser authentication for security reasons. This provides secure, interactive authentication through your web browser using SSO and identity providers like Okta, AD FS, or any SAML 2.0-compliant IdP. See Connecting to Snowflake with the Python Connector for more information about externalbrowser authentication.
- No. For security reasons, this MCP server only supports externalbrowser authentication. Password-based authentication, private key authentication, and other methods are not supported. The server will validate and enforce this requirement at startup.
- The MCP server is intended to be used as one part of the MCP ecosystem. Think of it as a collection of tools. You'll need an MCP Client to act as an orchestrator. See the MCP Introduction for more information.
- All tools in this MCP server are managed services, accessible via REST API. No separate remote service deployment is necessary. Instead, the current version of the server is intended to be started by the MCP client, such as Claude Desktop, Cursor, fast-agent, etc. By configuring these MCP client with the server, the application will spin up the server service for you. Future versions of the MCP server may be deployed as a remote service in the future.
- Ensure your Snowflake user has the appropriate permissions for the services you're trying to use. Contact your Snowflake administrator if you need additional role permissions or access to specific databases, schemas, or warehouses.
- You may add multiple instances of both services. The MCP Client will determine the appropriate one(s) to use based on the user's prompt.
- If your account name contains underscores, try using the dashed version of the URL.
- Account identifier with underscores:
acme-marketing_test_account - Account identifier with dashes:
acme-marketing-test-account
- Account identifier with underscores:
Please add issues to the GitHub repository.