GitOps ArgoCD Implementation: Automate Infrastructure Creation with Terraform & GitHub Actions, and Application Deployment on EKS Cluster
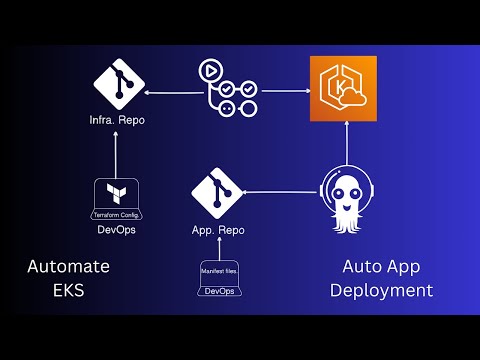
This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough for setting up a GitOps workflow. It uses Terraform and GitHub Actions to automate infrastructure provisioning on AWS EKS and leverages ArgoCD for automating application deployments.
- Overview
- Pre-requisites
- Step 1: Create GitHub Repositories
- Step 2: Configure GitHub Secrets
- Step 3: Configure Terraform for EKS Setup
- Step 4: Create GitHub Actions Workflow
- Step 5: Install ArgoCD on EKS Cluster
- Step 6: Access the ArgoCD UI
- Step 7: Configure ArgoCD for Automated Application Deployment
This guide will help you set up an automated GitOps pipeline:
- Automate Infrastructure: Use Terraform and GitHub Actions to provision an EKS cluster.
- Automate Application Deployment: Use ArgoCD to monitor the application repository and deploy updates to the EKS cluster automatically.
Watch the full tutorial on YouTube to follow along with step-by-step instructions.
- GitHub account to create repositories.
- AWS account with permissions to create EKS resources.
- AWS CLI installed and configured on your local machine.
- kubectl installed for Kubernetes cluster management.
- Create a GitHub repository called
infrastructureto store Terraform configurations. - Initialize the repository with a
README.mdfile.
- Create a separate GitHub repository called
applicationto store Kubernetes manifest files. - Initialize the repository with a
README.mdfile.
To authenticate GitHub Actions with AWS for infrastructure deployment:
- Go to your Infrastructure Repository in GitHub.
- Navigate to
Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions. - Add the following secrets:
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
These secrets are necessary for AWS authentication when GitHub Actions runs the Terraform configuration.
In the infrastructure repository, create the following Terraform files:
resource "aws_vpc" "main" {
cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"
enable_dns_hostnames = true
}
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "main" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
}
resource "aws_route_table" "main" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.main.id
}
route {
cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"
gateway_id = "local"
}
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "subnet_1_association" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet_1.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.main.id
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "subnet_2_association" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet_2.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.main.id
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "subnet_3_association" {
subnet_id = aws_subnet.subnet_3.id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.main.id
}
resource "aws_subnet" "subnet_1" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-south-1a"
map_public_ip_on_launch = true
}
resource "aws_subnet" "subnet_2" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
cidr_block = "10.0.2.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-south-1b"
map_public_ip_on_launch = true
}
resource "aws_subnet" "subnet_3" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
cidr_block = "10.0.3.0/24"
availability_zone = "ap-south-1c"
map_public_ip_on_launch = true
}
module "eks" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws"
version = "~> 20.0"
cluster_name = "my-cluster"
cluster_version = "1.31"
cluster_endpoint_public_access = true
cluster_addons = {
coredns = {}
eks-pod-identity-agent = {}
kube-proxy = {}
vpc-cni = {}
}
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
subnet_ids = [aws_subnet.subnet_1.id, aws_subnet.subnet_2.id, aws_subnet.subnet_3.id]
control_plane_subnet_ids = [aws_subnet.subnet_1.id, aws_subnet.subnet_2.id, aws_subnet.subnet_3.id]
eks_managed_node_groups = {
green = {
ami_type = "AL2023_x86_64_STANDARD"
instance_types = ["m5.xlarge"]
min_size = 1
max_size = 1
desired_size = 1
}
}
}terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 5.0"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-south-1"
}terraform {
backend "s3" {
bucket = "mir-terraform-s3-bucket"
key = "key/terraform.tfstate"
region = "ap-south-1"
}
}Push the code to your GitHub infrastructure repository:
git add .
git commit -m "Initial Terraform setup for EKS"
git push origin mainCreate a GitHub Actions workflow file to automate Terraform deployment.
name: Terraform CI/CD Pipeline
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches:
- main
jobs:
terraform:
name: Apply Terraform
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup Terraform
uses: hashicorp/setup-terraform@v2
with:
terraform_version: 1.5.6
- name: Configure AWS Credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v2
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Terraform Init
run: terraform init
- name: Terraform Plan
run: terraform plan
- name: Terraform Apply
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
run: terraform apply -auto-approveGitHub Actions will:
- Initialize Terraform.
- Plan the infrastructure.
- Apply changes to the
mainbranch.
-
Configure
kubectlto access your EKS cluster:aws eks update-kubeconfig --region ap-south-1 --name my-cluster kubectl cluster-info kubectl get nodes
-
Install ArgoCD:
kubectl create namespace argocd kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
-
Change the ArgoCD server service type to LoadBalancer:
kubectl patch svc argocd-server -n argocd -p '{"spec": {"type": "LoadBalancer"}}' -
Retrieve Initial Admin Credentials:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
-
Get the External IP of the ArgoCD server:
kubectl get svc argocd-server -n argocd
-
Access the ArgoCD UI by navigating to
http://<EXTERNAL-IP>in your browser. -
Login to ArgoCD:
- Username:
admin - Password: Retrieved from the previous step.
- Username:
-
Log in to ArgoCD UI.
-
Add a New Application:
- In ArgoCD UI, click on New App.
- Fill in the following details:
- Application Name:
my-app - Project:
default - Sync Policy: Automatic (if desired)
- Application Name:
- Source:
- Repository URL:
https://github.com/your-username/application - Revision:
main - Path:
/(or the relevant folder for manifests)
- Repository URL:
- Destination:
- Cluster:
https://kubernetes.default.svc - Namespace:
default(or any other)
- Cluster:
-
Save the configuration. ArgoCD will now monitor the application repository for changes and deploy them automatically to the EKS cluster.
By following this guide, you now have a fully automated GitOps pipeline using Terraform, GitHub Actions, and ArgoCD. Your EKS infrastructure is provisioned, and application deployments are automated through ArgoCD.
📝 Comprehensive Guide For a detailed guide, please refer to the Youtube video.